What is Laparoscopy?
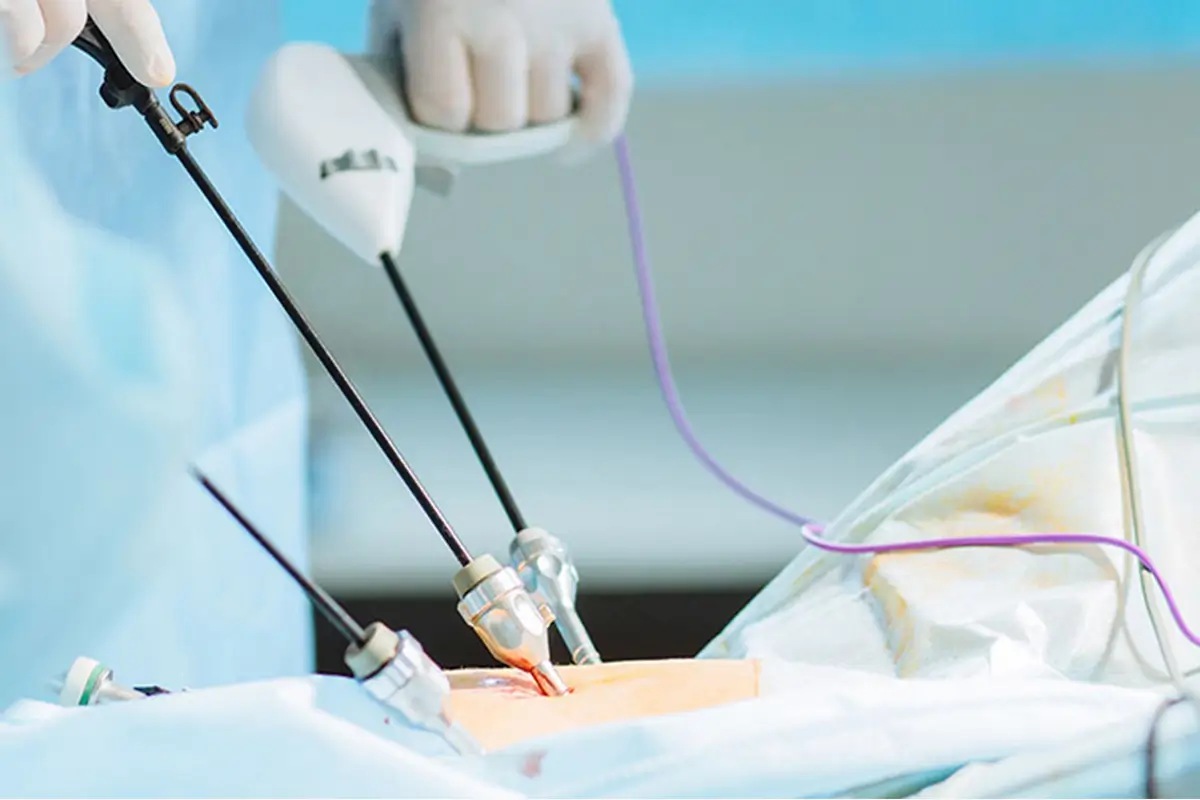
Laparoscopy is a modern surgical technique used to examine or treat the internal organs of the abdomen and pelvis using a specialized instrument called a laparoscope. In this procedure, instead of large surgical incisions, several small incisions are made on the body, and the surgery is performed with minimal tissue damage.
Applications of Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy has a wide range of applications in the medical field and is used for the diagnosis and treatment of many conditions. Some of the most important uses of this technique include:
- Removal of cysts, fibroids, and other masses
- Treatment of endometriosis and ectopic pregnancy
- Performing bariatric surgeries for weight loss
- Hernia repair or treatment of intestinal problems
- Removal of organs such as the gallbladder, spleen, or kidney
- Diagnostic procedures
The Laparoscopic Procedure
To perform this surgery, carbon dioxide gas is first introduced into the abdomen to create the necessary space for better visualization and more precise surgery. Then, using a small camera and specialized instruments inserted through the small incisions, detailed and live images are transmitted to a monitor, allowing the surgeon to perform the surgery with high accuracy.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Laparoscopy
This technique has gained significant attention for several reasons. The advantages of laparoscopy include:
- Smaller incisions and reduced postoperative pain
- Shorter recovery period compared to traditional open surgery
- Reduced risk of infection and other complications
However, its potential disadvantages include:
- The need for advanced equipment and a high level of surgical skill
- Not being suitable for some complex surgeries or specific cases
Postoperative Care After Laparoscopy
After surgery, following the doctor’s recommendations is crucial. During the recovery period, the patient should avoid strenuous activities, take prescribed medications, and consult a doctor immediately if symptoms such as fever or severe pain are observed.